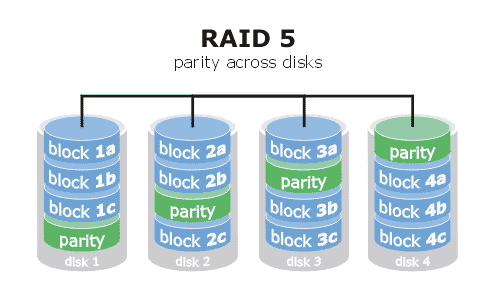
Con l’arrivo di nuovi hard disk e con il continuo spostamento di cartelle da un disco all’altro del server per gestire lo spazio disponibile ho deciso finalmente di crearmi un RAID5 sfruttando il controller intel P55 integrato nella scheda madre del server (una Asus P7P55D-E).
Informandomi prima in rete, sembrava che le prestazioni dei controller integrati non fossero cosi buone, con esperienze di gente che parlava di 20, massimo 30mb/s in scrittura. Decisamente poco!!
Ho deciso comunque di rischiare, e cosi domenica sera ho creato tramite l’utility del bios della Intel un RAID5 formato da 4 dischi Western Digital Green da 2TB l’uno.
Con una configurazione RAID5, lo spazio a disposizione è di Ndischi-1, quindi con 4x2tb dovrebbe essere 6TB.
C’è però da tenere conto che una volta formattato il volume, lo spazio a disposizione sarà di 5.5TB circa (fate i vostri conti sulla convenienza).
 Con l’arrivo di nuovi hard disk e con il continuo spostamento di cartelle da un disco all’altro del server per gestire lo spazio disponibile ho deciso finalmente di crearmi un RAID5 sfruttando il controller intel P55 integrato nella scheda madre del server (una Asus P7P55D-E).
Con l’arrivo di nuovi hard disk e con il continuo spostamento di cartelle da un disco all’altro del server per gestire lo spazio disponibile ho deciso finalmente di crearmi un RAID5 sfruttando il controller intel P55 integrato nella scheda madre del server (una Asus P7P55D-E).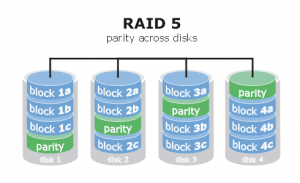

![php[1]](http://www.smartdomotik.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/02/php1-300x208.jpg)


 Con il passaggio di dominio ad uno personalizzato mi si è reso necessario la creazione di un certificato SSL per permettere l’utilizzo di comunicazioni HTTPS sul mio dominio.
Con il passaggio di dominio ad uno personalizzato mi si è reso necessario la creazione di un certificato SSL per permettere l’utilizzo di comunicazioni HTTPS sul mio dominio.




